How Your Credit Score Can Affect Your Interest Rates

Your credit score is the primary factor in determining the interest rates creditors will charge you. Your credit score, good or bad, reflects your credit history. So the higher your credit score, the less of a risk you pose to the lender. If you have a low credit score, creditors will charge higher interest rates, along with fees and deposits, to compensate for the risk of you potentially defaulting on the loan or missing payments.
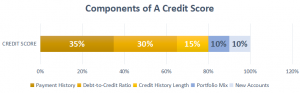
Credit Score & its Components
- Perfect credit score: 850
- Excellent rating: 740-849
- Good credit score: 700 to 739
- Fair score: 650 to 699
- Low score: 649 and below
The Pain of Higher Interest Rates
Why should you worry about higher interest rates? In one word, money. Lots of money. The difference between an interest rate of 1% or 2% doesn’t sound like much. Sometimes it doesn’t even make that much of a difference on your monthly payment. But every one percent increase on a $100,000 loan is equivalent to $68,000 in interest payments. In today’s market, if you have a FICO score of 680, you will pay almost two percentage points more on your interest rate. That could mean a difference of almost $200,000 in interest payments over the life time of your loan. What would you do with $200,000?
Qualify for Better Rates
Maintaining an excellent credit rating is the only way to obtain the best interest rate when purchasing anything big or small. So it’s important to understand FICO score risk factors. Contact Roundleaf Inc. to see how we can help you raise your credit score and qualify for better financing!
